Table of Contents
ToggleHam Radio Distance: Why Your Radio Gets Poor Range and How to Resolve It
On Friday last week, as I geared up for a new adventure with my friend Motorola GP338 in tow; something felt amiss. A walkie-talkie that sped to over half a mile away in crystal-clear sound earlier felt like it was dragging its feet this time around. It lasted only 500 meters and left me disappointed thinking where I had it wrong. This situation is so predominant in the world of radio, particularly ham radio distance. Whether you are a ham radio by trade or just using it for that weekend trip, knowing the reason behind your low range is very important. So, let us drill down into the details on how to fix it up.
The Usual Suspects: Common Causes of Poor Radio Range

Like the turning of enemy robots upon you, we cannot react (too well) to disrupt our foes satellite hardware and instead have to consider among a number factors that result in poor radio range. One or more of these reasons are very likely contributing.
1. Obstacles and Terrain
Imagine trying to transmit a message but being obstructed by a skyscraper or mountain. Tall buildings, hills, and dense forests function as barriers, blocking or deflecting your signal. This is particularly true for VHF (Very High Frequency) waves, which struggle to penetrate solid surfaces. UHF (Ultra High Frequency) transmissions, on the other hand, may manage obstructions more effectively but have lesser ranges in broad regions. There are many variables that can influence each of these and the best way to troubleshoot poor performance is understanding how they impact your ham radio distance.
Click here if you have any doubt about which ham radio to buy, the VHF or UHF advantages and disadvantages and know what kind of equipment best suits your needs.
2. Antenna Antics
Comm Range- This is pretty self explanatory in that the antenna on your radio plays a large role. Your ham radio range will be highly limited if you use a broken or cheap stock antenna. Now consider the fact that even just holding your radio wrong can degrade performance. Check to ensure that the antenna is upright and that you are using the correct frequency-specific VHF or UHF antenna. Furthermore, if you use an external antenna, how it is positioned and orientated might determine your range.
Yes, antennas play a crucial role in radio communication. They significantly impact the range and quality of your signal. Find out how antennas can enhance your radio experience here.
3. Battery Blues
The thing about radios is that they need batteries. An old, weak battery will reduce how much power the radio can transmit and then it may not get as far. However, if your radio is near the end of its battery life, it will not be able to broadcast at full power and being a ham Radio distance will be just that,a distant dream. Regularly verify the status of your batteries and make sure they are charged, consider acquiring high-capacity or lithium-ion batteries for long-term use.
Find out what the best field batteries are for your outdoor ham radio. Head here to determine which one is best for you.
4. Frequency Fiascos
Choosing the proper frequency is like selecting the ideal tool for the job. VHF frequencies perform well in open regions with little impediments, but UHF frequencies thrive in urban settings. However, be aware of interference from other electrical devices and users. The improper frequency can dramatically restrict your range, much like attempting to conduct a conversation at a loud concert. Assess your surroundings and select the best frequency to optimize your ham radio range.
Follow the radio frequency chart to find the proper frequency for your ham radio. Learn more here.
5. Environmental Factors
Mother Nature has her own thoughts regarding your communication requirements. Rain, snow, and fog can all significantly reduce your signal’s range. Furthermore, neighboring electronic equipment, such as routers and cellphones, might generate interference, lowering your ham radio range. While you cannot control the weather, you may reduce interference by changing to less congested channels or utilizing CTCSS (Continuous Tone-Coded Squelch System) or DCS (Digital Coded Squelch) codes for a cleaner connection.
Practical Solutions to Boost Your Radio Range
If you already know what is the reason for your radio to work so badly, then let’s take a look at some alternatives. Below are a few practical steps that you can take to help maintain or increase your ham radio range.
1. Improve Your Line of Sight
Radio transmissions thrive in wide open areas. If you can, move to an area with fewer obstructions — getting your radio up a little higher or finding taller ground will vastly improve how far the other person(s) can communicate. When indoors, head outdoors or move somewhere with fewer walls between you and the person at your other end of conversation. This is very important for ham radio operators who wish to transmit long distance.
2. Use Repeaters and Boosters
Repeaters and signal boosters can either be necessary (when simple repairs are not enough) or simply work to enhance an existing transmitter hotspot. Repeaters pass your signal along over greater distances, allowing you to project information further. Great Boon also for Ham radio operators who are willing to beat the limits of ham radio distance. On the other hand, signal boosters can amplify your radio’s output power so that it becomes stronger and more immune to interference.
Need help setting up a repeater? Check here for the guide to amateur radio repeaters.
3. Upgrade Your Antenna
Your antenna is a crucial component in increasing ham radio distance. If you’re still using the stock antenna that came with your radio, consider upgrading to a high-gain or aftermarket antenna optimized for your frequency band. A stronger antenna may greatly increase your range, particularly in difficult conditions like dense forests or metropolitan areas.
4. Maintain Your Equipment
The systems need constant help for best performance. Occasionally inspect your radio, and equipment for signs of wear. Always verify that your antenna is well seated, the battery is working correctly and check radio settings for best performance. In our ways firmware upgrades have been able to perform the same where we can increase speed one way or another, therefore keep your radio up-to-date.
5. Consider Upgrading Your Radio
Alright, this is a bit tough love for us but sometimes — it may not be where or how we are using our radio. Default tuning may not offer the max range (Unoptimized systems, too low quality devices). In the case that you have attempted everything else and after all of this are not content with your ham radio range, there might be a requirement for an upgrade to a newer model which provides better mileage as well as more features along-side longer battery life.
Common Myths About Radio Range

There are several myths and misconceptions around radio range. Let’s go over some of the most popular ones to assist you learn how to get greater ham radio distance.
1. More Power Equals More Range
While additional strength might help you go further, it is not a cure-all. Increasing your radio’s power output can assist, but only to a certain extent. Other elements that influence your total range include barriers, antenna quality, and frequency choices. Simply increasing the wattage will not overcome these obstacles.
2. Any Antenna Will Do
Not all antennas are made equally. The appropriate antenna for your radio is determined by the frequency, operating conditions, and desired range. A high-gain antenna built for VHF frequencies will not always boost your range if you’re using UHF frequencies. Make sure your antenna is appropriate for your radio’s needs.
3. Weather Doesn’t Affect Range
Radio frequencies, especially HF, can be affected by weather. And rain, snow, fog or even high humidity might reduce the signal affecting your ham radio range. You may not be able to change the weather, but you can certainly modify what and how you operate in order to lessen its effects — relocating or using higher frequency bands that have less atmospheric influence being two prime examples.
Ham Radio Distance: A Closer Look
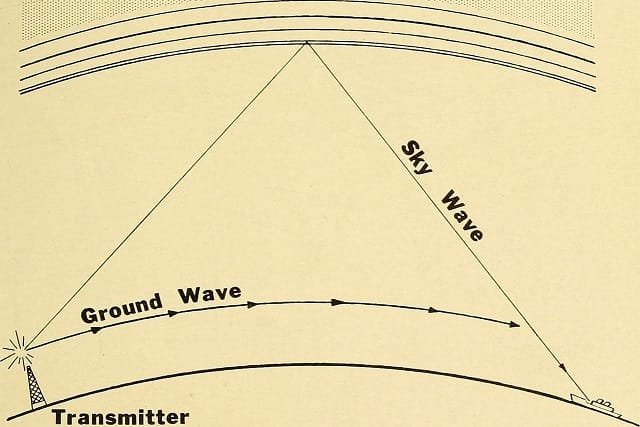
Now that we’ve covered the fundamentals, let’s get into ham radio distance specifically. Ham radio operators frequently encounter distinct obstacles in terms of range, particularly when communicating over great distances. Here’s how to increase your ham radio range.
1. Understanding Propagation
Different radio wavelengths allow travel in different paths based on their frequency, geography and climatic condition. The ionosphere enables some of our longest-distance transmissions; for example, HF (high frequency) radio signals frequently employed in ham radio operate within this range. This is why amateur radio operators are able to communicate with each other internationally in a manner that (most of the time) makes it look as though we have free long-distance calling. A knowledge of propagation will allow you to choose the ideal frequency and time for optimizing your ham radio range.
2. Using High-Gain Antennas
High-gain antennas direct your radio’s radiation in a specified direction, boosting its range. Using a directional antenna, such as a Yagi, may dramatically enhance ham radio distance, especially when attempting to contact faraway stations. These antennas are perfect for long-distance transmission, but they need precise aiming and configuration.
3. Utilizing Repeaters
Repeater: This is a ham radio operator’s best friend to give more range on your ham radios. This signal extends far greater distances than a radio by taking a merely micro watt output of the walkie talkies and receiving your conversation re-transmit it at much higher power levels. Most localities have repeater networks for use by ham radio operators to extend the range of communication.
Final Thoughts: Mastering Radio Range
Poor radio range might be aggravating, but it is not an insurmountable issue. Understanding the variables that influence your range and taking efforts to solve them will greatly enhance your ham radio distance and overall communication experience. Whether you’re dealing with urban obstructions, dense woodlands, or poor batteries, there’s always a method to restore your radio back to its peak performance.
Check out TalkieTrail.com for additional tips, techniques, and in-depth information on anything from walkie-talkies to ham radios. With the appropriate information and a little effort, you can transform poor range into effective communication. Happy talking!


